JAMA Clinical Reviews
Author interviews that explore the latest clinical reviews.
Semaglutide has recently been shown to induce clinically significant weight loss in patients with obesity that is sustained for as long as the drug is given. Tom Wadden, PhD, from the University of Pennsylvania, discusses results from the series of recent STEP trials and how they compare to the effects of other medications used to treat obesity.
Related Articles:
Performing repeated statistical comparisons on data can result in false-positive findings. Jing Cao, PhD, associate professor of statistics at Southern Methodist University, explains problems that can arise from multiple testing procedures and how to avoid making false conclusions.
Related Article:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a clinical syndrome of vague abdominal pain and cramping associated with diarrhea or constipation. IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion, and a variety of treatments can improve its symptoms. Michael Camilleri, MD, professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, discusses recent advances in the diagnosis and management of IBS.
Related Article:
Advance directives (ADs) allow patients to express their medical treatment preferences. Patients with ADs are more likely to receive medical care concordant with their wishes and are less likely to die in the hospital than patients without them, but use remains low in the US. Maria Silvera, MD, a palliative care physician and associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, and Catherine Auriemma, MD, a fellow in pulmonary/critical care medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, discuss the importance of ADs and strategies to increase their uptake.
Related Article:
The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are the first of many being tested for widespread use. Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program, reviews these and other vaccines likely to become available, including products that use inactivated, protein subunit, and viral vector immunization strategies.
Related Content:
The CDC coordinated a massive effort to immunize nearly all nursing home and long-term care facility residents in the US against COVID-19 infection in the month after vaccine approval. Ruth Link-Gelles, PhD, MPH, CDC staff epidemiologist and Lieutenant Commander of the US Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, describes how.
Related Article(s):
Nursing Homes’ Next Test—Vaccinating Workers Against COVID-19
Highly effective B-cell therapies like rituximab and ofatumumab have changed the outlook for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Alexander Rae-Grant, MD, emeritus professor of neurology at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, discusses recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of MS.
Related Article(s):
Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other social systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color. Mitchell Katz, MD, president and chief executive officer of NYC Health + Hospitals, the largest US public health care system, is an expert in health care delivery to disadvantaged populations. He explains how structural racism worsens health outcomes and what health systems can do to address it.
Related:
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in COVID-19
The Winter COVID-19 Surge in New York and Los Angeles
Diversifying Medical Education
Surgeon Creates Barrier-Free COVID-19 Testing Service for Philadelphia's Black Residents
Taking a Closer Look at COVID-19, Health Inequities, and Racism
Recalibrating the Use of Race in Medical Research
Responding to COVID-19 With a Structurally Competent Health Care System
Natural experiments comparing coronavirus spread on ships and in hair salons with vs without face masks point to the importance of wearing masks for curbing SARS-CoV-2 spread. John T. Brooks, MD, chief medical officer of the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, reviews recently published epidemiologic data that reinforce the role of mask use for pandemic control.
Related Article:
Effectiveness of Mask Wearing to Control Community Spread of SARS-CoV-2
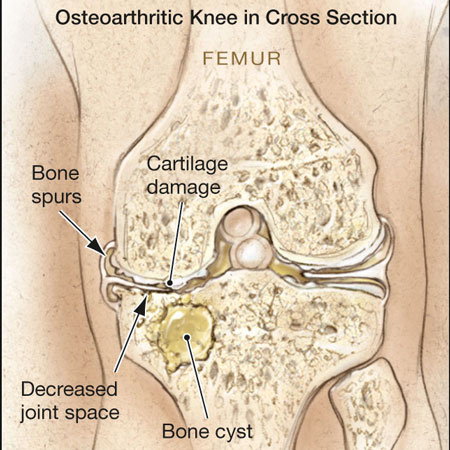
Philip Cohen, MD, associate clinical professor of internal medicine at UCLA, a primary care internist who also specializes in sports medicine, discusses the primary care management of osteoarthritis.
Related Articles:
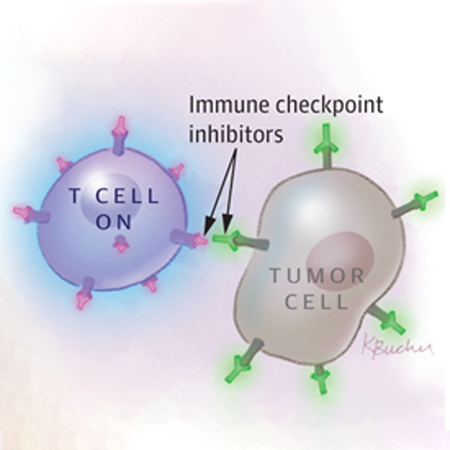
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have been a major breakthrough in cancer treatment but can have many serious adverse effects. Pankti Reid, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine in rheumatology at the University of Chicago, discusses the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of toxicities from immune checkpoint inhibitors as outlined by the 2019 NCCN guidelines.
Related Article:
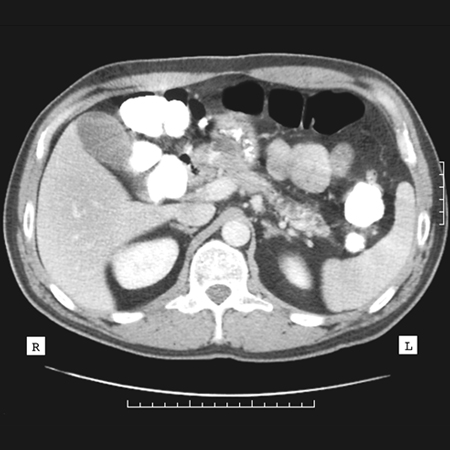
Howard Reber, MD, emeritus professor of surgery at UCLA, discusses how to treat acute pancreatitis.
Related Article(s):
Howard Reber, MD, emeritus professor of surgery at UCLA, discusses how to diagnose acute pancreatitis.
Related Article(s):
Ethnic and racial minorities have been particularly hard hit with COVID-19 in some communities. Mitchell Katz, MD, president and chief executive officer of New York City Health + Hospitals, and former Los Angeles County health agency director, discusses this problem and what has been learned from COVID-19 that can help resolve the general problem of health care disparities.
Related Article:
Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable disease and death in the world, but most attempts to quit are unsuccessful. Atul Jain, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo College of Medicine, discusses new guidelines from the American Thoracic Society on pharmacologic management of tobacco cessation, including target population and deciding when to initiate.
Related Article(s):
Initiating Pharmacologic Treatment in Tobacco-Dependent Adults
Mitchell Katz, MD, president and chief executive officer of New York City Health + Hospitals, and former Los Angeles County health agency director, discusses causes, similarities, and differences between the spike of COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the 2 cities.
Related Article:
Modernize Medical Licensing, and Credentialing, Too—Lessons From the COVID-19 Pandemic
Glaucoma is the most common cause of irreversible blindness in the world. Joshua Stein, MD, MS, associate professor of ophthalmology at the University of Michigan, reviews the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma.
Related Article:
A new trial reports that a third of emergency department patients presenting with appendicitis admitted for oral antibiotic treatment had outcomes no different from those admitted for intravenous antibiotic treatment. Paulina Salminen, MD, PhD, professor of surgery at the University of Turku in Finland, discusses the findings.
Related Article(s):
Gregory Armstrong, MD, director of the Advanced Molecular Detection Program for the CDC, explains what is currently known about the new mutations of SARS-CoV-2.
Related Article(s):
Next-generation sequencing is a catchall term for new, high-throughput technologies that allow rapid sequencing of a full genome. It can be used to sequence a patient’s DNA in diagnosing a genetic disorder or characterizing a cancer, but it can also be used to sequence the genome of a pathogenic bacteria, virus, fungi, or parasites. In this JAMA clinical review podcast, we talk with authors Marta Gwinn, MD, MPH, and Gregory L. Armstrong, MD, from the CDC, about how next-generation sequencing of infectious pathogens is being implemented in clinical practice and in public health surveillance for infectious disease.
Related Article(s):
Next-Generation Sequencing of Infectious Pathogens
Podcast originally published 2/14/19.
Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, and Sara Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, from the CDC discuss rare allergic complications in patients who received the first dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine between December 14-23, 2020.
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an often overlooked cause of acute ischemic stroke. JAMA Associate Editor Jeffrey Saver, MD, professor of neurology at UCLA, discusses new recommendations from a 2020 AAN Practice Advisory about use of mechanical PFO closure and anticoagulant vs antiplatelet therapy to prevent subsequent strokes in patients with a PFO and an initial event.
Related Article:
Management of Patients With a Patent Foramen Ovale With History of Stroke or TIA
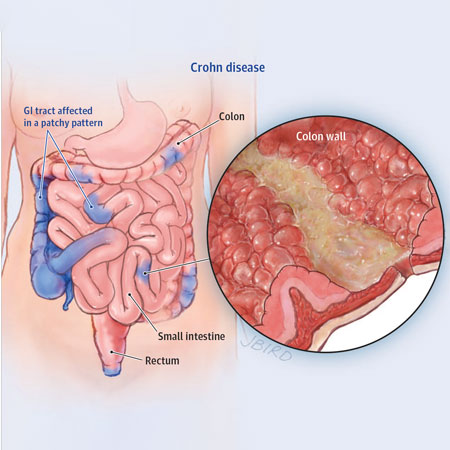
New therapies have greatly improved outcomes for patients with Crohn disease. Peter Higgins, MD, from the University of Michigan, discusses advances in management and treatment protocols.
Related Article:
Management of Crohn Disease
Dr. Adam Lauring from the University of Michigan Division of Infectious Diseases, an expert on the evolutionary biology of RNA viruses, explains the new genetic variants recently found in SARS-CoV-2 and their importance.
Elderly persons and residents of nursing homes have been the hardest hit in the COVID-19 pandemic. Harvard geriatrician Sharon Inouye, MD, discusses the effect COVID-19 has had on nursing homes and what should be done about it.
Related Article:
Homeless patients with chronic medical conditions who need long-term care often repeatedly present to emergency departments to receive treatment. Following a performance improvement analysis, clinicians at UCSF developed an emergency department–based team who work with the community to provide care for this challenging population. Hemal Kanzaria, MD, and Jack Chase, MD, discuss how UCSF has addressed this clinical problem.
Related Article(s):
Caring for Emergency Department Patients With Complex Medical, Behavioral Health, and Social Needs
JAMA Fishbein Fellow Kristin Walter, MD, interviews Craig Garfield, MD and Richard Weissbourd, MD, about parental relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Related Article(s):
Considerations for Young Children and Those With Special Needs as COVID-19 Continues
Lockdowns resulting from COVID-19 have had a devastating effect on everyone’s personal lives and the economy. What factors in people’s daily lives are most associated with SARS-CoV-2 transmission between people? Manish Patel, MD, team lead of the CDC’s Influenza Prevention & Control Team, discusses a study they conducted examining what sorts of activities might be associated with COVID-19 disease transmission.
Related Article(s):
Community Outbreak Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Among Bus Riders in Eastern China
It is well known that alcohol use severely affects driving ability, but does cannabis? There are many fewer traffic crashes related to cannabis than alcohol intoxication. Johannes Ramaekers, PhD, of the University of Maastricht in the Netherlands, discusses his study examining the relationship between vaping THC and driving safety.
Related Articles:
Effect of Cannabidiol and Δ-Tetrahydrocannabinol on Driving Performance
Driving Under the Influence of CBD or THC—Is There a Difference?
Closing businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic has had devastating consequences for individuals and the economy in general. Proper air handling combined with the use of masks and physical distancing can greatly improve the safety of indoor spaces. Joseph Allen, DSc, MPH, assistant professor of exposure assessment science at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and Andrew Ibrahim, MD, assistant professor of surgery and architecture and urban planning at the University of Michigan, discuss air conditioning standards that can substantially reduce the risk of disease transmission in indoor spaces.
Related Article(s):
Roger J. Lewis, MD, PhD, discusses Randomization in Clinical Trials from the JAMA Guide to Statistics and Methods
Related Article(s):
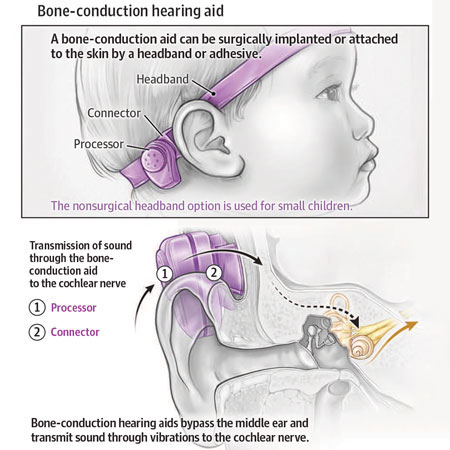
Judith Lieu, MD, from the Department of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery at Washington University in St Louis, discusses the need for screening young children for hearing loss and the importance of treating hearing loss as early in life as is possible.
Related Article:
Certificates of Need are regulations required by some states before any construction or expansion of services at medical facilities are undertaken. Originally developed to prevent excessive construction of expensive health care facilities, these rules have distorted health care markets and probably should be repealed. Karl Bilimoria, MD, from Northwestern University, Tarik K Yuce, MD, and JAMA Associate Editor Karen Joynt Maddox, MD, from Washington University, discuss the current status of these regulations and their effect on health care markets.
Related Article(s):
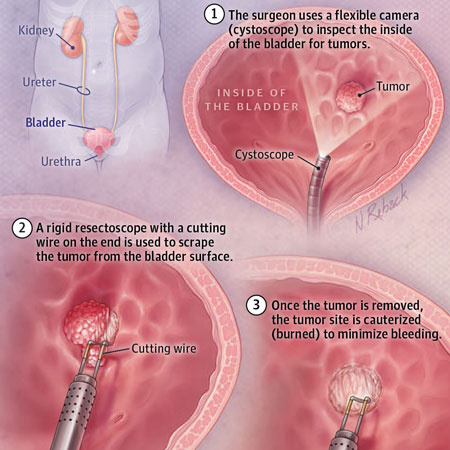
Mark Litwin, MD, chair of Urology at the UCLA School of Medicine, discusses the evaluation of hematuria and also the presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of bladder cancer.
Related Article(s):
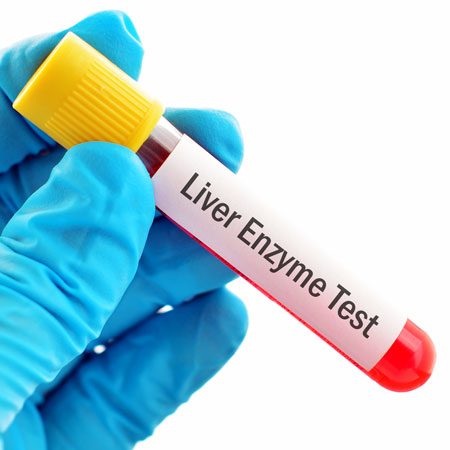
There are hundreds of thousands of liver transplant patients, all of whom will be seen in general clinical practices. It is common for them to develop elevated liver enzymes--a potentially serious problem that may be a sign that the transplanted liver is failing. Traditionally, patients with these findings are sent to a liver transplant center for an inpatient workup. A new protocol facilitating management of most of these patients in routine outpatient clinics has been developed, greatly improving the efficiency of managing patients with this clinical problem. Fady Kaldas, MD, director of the Dumont-UCLA transplant center, discusses how to manage elevated liver function results in liver transplant patients on an outpatient basis.
Related Article(s):
Outpatient Management of Liver Function Test Abnormalities in Patients With a Liver Transplant
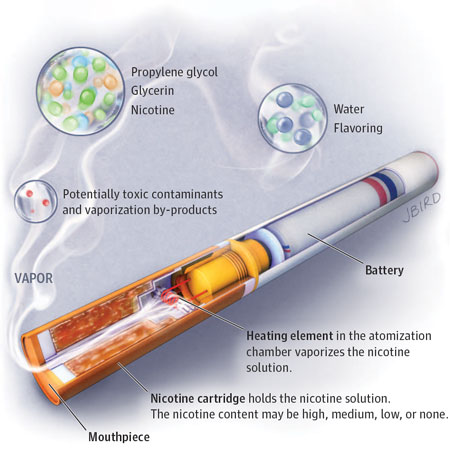
Are e-cigarettes helpful or harmful as a tool to help people stop smoking? Mark J. Eisenberg, MD, MPH, from the Jewish General Hospital and McGill University in Montreal, Canada, discuss a recent clinical trial he reported in the November 10, 2020, issue of JAMA examining the efficacy of e-cigarettes as a smoking cessation aid.
Related Article:
Effect of e-Cigarettes Plus Counseling vs Counseling Alone on Smoking Cessation
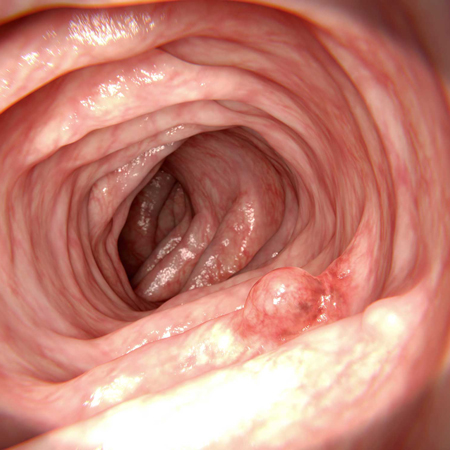
A new multisociety guideline was recently released suggesting that for many patients, the interval between colonoscopies following polyp resection is less than previously recommended. Cecelia Zhang, MD, Duke University, and Maylyn Martinez, MD, University of Chicago, discuss the new guideline.
Related Article:
Tim Uyeki, MD, chief medical officer for the Influenza Division, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), discusses how the COVID-19 pandemic may affect the 2020-2021 influenza season.
Related Article(s):
The Platelet Inhibition and Patient Outcomes (PLATO) trial showed that ticagrelor had better outcomes than clopidogrel for avoiding thrombotic complications following acute coronary syndrome. Subsequent trials suggested that the outcomes for the drugs were about the same. The effects of ticagrelor and clopidogrel were examined in a very large observational study performed by Harlan Krumholz, MD, and colleagues, published in the October 27, 2020, issue of JAMA. Dr Krumholz explains how his study was performed and what it showed.
Related Article:
Many people are hoping that enough people develop resistance to COVID-19, either from being exposed to the disease or from vaccination, to develop herd immunity that will enable society to return to normal. But will that happen? Saad Omer, MD, from the Yale Institute for Global Health, discusses his JAMA article on herd immunity and how much we can count on having it to return society to normal from this COVID-19 pandemic.
Related Article(s):
David Juurlink, MD, PhD, a clinical pharmacologist and professor of internal medicine at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre and professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, discusses 10 things new doctors should know about drugs and thir complications as they start practicing medications in the the fourth and final episode of this series.
One of the most important things clinicians can do is help patients and their families deal with impending death. Despite its importance, this part of medical care is hardly covered in medical training. Clinicians have to learn this on their own. One of the most powerful ways to find out what it’s like is to go through it yourself. Martin F. Shapiro, MD, professor of medicine at the Weill Cornell School of Medicine, describes along with his sister, Lori Shapiro, what they went through in dealing with their mother’s death. Dr Shapiro relates what he learned to more effectively manage his patients and their families in coping with the end of life.
Related Article(s):
Sweden’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic differed from its neighbors in Europe. Lockdowns were minimized with the belief that they would be more damaging than the virus itself. Much criticism was levied at the country regarding these policies. Anders Tegnell, MD, is the head of the Department of Public Health Analysis and Data Management, Deputy Director General at the Public Health Agency of Sweden, and had been Sweden's state epidemiologist since 2013. He discusses what Sweden did in response to COVID-19 and what their outcomes were.
Related Article:
In the 13 years since the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America have issued guidelines for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia much has changed, resulting in a new guideline with 16 major recommendations. These are reviewed by Maylyn Martinez, MD, from the Department of Medicine at the University of Chicago and JAMA Network Open Associate Editor Angel Desai, MD, from the Department of Medicine at the University of California at Davis.
Related Article:
Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults With Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Intimate partner violence--also known as domestic abuse--may affect as many as 1 in 3 women. It’s often underreported but that shouldn’t be the case. Harriet L. MacMillan, MD, from the Departments of Psychiatry & Behavioral Neurosciences and Pediatrics at McMaster University, discusses how to identify and intervene in intimate partner violence.
Related Article(s):
When trying to administer its qualifying examination during the COVID-19 shutdowns, the American Board of Surgery failed. Jo Buyske, MD, president and chief executive officer of the American Board of Surgery, discusses what went wrong and what they are doing to fix it.
Related Article:
A new clinical trial suggests that obstructive sleep apnea is better treated with airway surgery than by medical treatment. The author of the study published in JAMA, Stuart MacKay, MBBS, from the University of Wollongong, Australia, discusses the study and treatments for obstructive sleep apnea.
Related Article:
Cluster randomized trials are performed when an intervention must be delivered to a group of patients like when testing new nursing protocols on award or different means for cleaning beds on a ward. One type of cluster trials is called a stepped-wedge where every cluster in the study ultimately undergoes the intervention. How this works it is explained by Susan Ellenberg, PhD, from the Department of Biostatistics, Epidemiology, and Informatics at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine.
Related Article:
Bariatric surgery is unequivocally the most effective means for inducing weight loss and managing diabetes for obese patients. There are numerous other benefits for these operations including improved long-term cardiovascular outcomes. David Arterburn, MD, MPH, a senior investigator from the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, discusses bariatric surgery outcomes.
Related Article(s):
COVID-19 continues to rapidly spread throughout the world. In the past few months, the population affected by the disease has shifted from older to younger patients. Public health officials are concerned that younger people seem not to be very compliant with recommendations regarding masking and social distancing. It is believed that younger people think that the adverse consequences of the disease occur in the elderly and not in them. Garret Salzman, MD, is a resident physician at UCLA and contracted the disease. He is young and healthy, but he has had substantial disability from COVID-19. He tells a cautionary tale of his experience with COVID-19 that this is not a benign disease in young people, that they need to be careful.
Related Article:
Potential Implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 Residency Application Cycle
The new American College of Gastroenterology guideline on ulcerative colitis is discussed by one of its authors, David T. Rubin, MD, from the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at the University of Chicago, and Maylyn Martinez, MD, also from the University of Chicago.
Related Article(s):
Acute pancreatitis can be a devastating disease. Complications of pancreatitis can be minimized by appropriate early, initial management. Joe Hines, MD, and Raman Muthusamy, MD, from UCLA discuss the recent American Gastroenterological Association guideline on managing acute pancreatitis.
Related Article(s):
Patients with serious disease fear the unknown. A physician with a serious disease knows the potential outcomes, making it far more difficult to cope. How does a physician react to developing cancer? Adam Stern, MD, an assistant professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, developed metastatic renal cell carcinoma when he was just 33 years old. He wrote about his experiences as a cancer patient in a Piece of My Mind article in the March 3, 2020, issue of JAMA and spoke about this to JAMA Clinical Reviews.
Related Article(s):
Before COVID-19, even though most children got vaccinated for measles, too many did not, resulting in worsening outbreaks of measles. People forgot how bad a disease measles is and became lax about getting their children vaccinated. Now in the COVID-19 era everyone is aware of what an out-of-control infectious disease can do and we are all anxiously awaiting a COVID-19 vaccine. Will this experience help encourage parents to get their children vaccinated? We discussed the problems of an adequate measles vaccination with Dr. Saad Omer, PhD, from the Yale Institute for Global Health at Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut.
Related Article(s):
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread throughout the world, flu season is almost upon us. This is concerning because there will be an overlap between flu and COVID-19 and patients could get both diseases. Daniel Solomon, MD, from the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital of the Harvard Medical School in Boston, discusses COVID-19 and how the flu might pan out this year.
Related Article:
One of the most contentious issues relating to COVID-19 is when to reopen schools. This is a complicated matter because placing people in close quarters risks spread of the disease. Yet children being at home makes it difficult for their working parents to manage their affairs and can potentially affect the learning experience. JAMA Associate Editor Preeti Malani, MD, chief health officer for the University of Michigan, discusses school reopening and how the University of Michigan is addressing this problem.
Related Article:
Association Between Statewide School Closure and COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality in the US
The use of hydroxychloroquine as a treatment for COVID-19 serves as an example of what is wrong with medical information being widely disseminated before it is thoroughly vetted by peer review. Preliminary studies of this treatment modality were spread widely, creating false hope that a treatment for COVID-19 existed. Several randomized trials have shown that hydroxychloroquine is not an effective therapy for COVID-19.
David Juurlink, MD, PhD, from the University of Toronto summarizes the evidence base regarding hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19.
Related Article(s):
Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
A major study recently published in JAMA showed that many children who have appendicitis do not need surgery and, if they undergo surgery, may have more disability than if they were treated with antibiotics alone. JAMA Clinical Reviews spoke with a patient in the study whose mother happens to be JAMA Associate Editor Preeti Malani, MD, JAMA’s infectious diseases editor and chief health officer for the University of Michigan. This patient initially was treated with antibiotics, later required appendectomy, and discussed the difficulties he experienced following laparoscopic appendectomy.
Related Article:
The European Society of Cardiology updated its guidelines for pulmonary embolism in 2019. Jonathan Paul, MD, from the University of Chicago discusses what is new in the management of pulmonary embolism based on his August 11, 2020, JAMA Guidelines Synopsis article.
Related Article(s):
Before a study is carried out, it is important to define what is an important difference between groups. This is often not done correctly. Anna McGlothlin, PhD, from Berry Consultants discusses how to assess the minimal clinically important difference in research studies.
Few treatments have proven to be effective for treating COVID-19. Recently, a clinical trial reporting the results of dexamethasone for treating COVID-19 was published and has received a great deal of attention in the popular media. Greg Curfman, MD, JAMA Deputy Editor, reviews the study and discusses what the findings do or do not reveal about the efficacy of dexamethasone for treating COVID-19.
Related Article(s):
Congestive heart failure is common and can have devastating effects on patients' quality of life. Until recently few treatments were available, but that has changed. Congestive heart failure management has substantially improved. Hutter Family Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School James L. Januzzi Jr, MD, reviews the diagnosis and treatment of congestive heart failure.
Related Article(s):
Accumulating evidence in adults has shown that nonoperative treatment of appendicitis is an acceptable means for treatment. A recent prospective study published in JAMA has shown the same is true for children. Most children who are treated with antibiotics instead of surgery for appendicitis do just fine. The lead author for this study, Peter Minneci, MD, from the Nationwide Children’s Hospital of the Ohio State Medical School, discusses his work in investigating alternative ways to treat appendicitis.
Related Article:
Some of the nearly 40 000 deaths each year in the US from breast cancer might be avoided through use of medications to prevent breast cancer in high-risk women. Patricia Ganz, MD, Distinguished Professor of Medicine and Public Health at UCLA, reviews the evidence underlying chemoprevention of breast cancer and which women might benefit from the drugs.
Related Article(s):
Medications for Primary Prevention of Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Risk Calculators:
https://bcrisktool.cancer.gov/calculator.html
https://tools.bcsc-scc.org/BC5yearRisk/intro.htm
https://ibis.ikonopedia.com/
Jeffrey Berger, MD, from the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at the New York University School of Medicine, explains the ins and outs of perioperative cardiovascular risk assessment and management for noncardiac surgery.
Related Article(s):
Perioperative Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Management for Noncardiac Surgery
Both remdesivir and dexamethasone have been promoted as effective treatments for COVID-19. JAMA Deputy Editor Greg Curfman, MD, and Professor Rachel Sachs, JD, from the Washington University School of Law discuss the science and health policy aspects of these COVID-19 treatments.
Related Article(s):
Whether the SARS-CoV-2 virus is transmitted by droplets or aerosol influences which public health interventions might slow its spread. Michael Klompas, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, explains evidence to date about mechanisms of coronavirus transmission and implications for pandemic containment and mitigation efforts.
Related:
Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Theoretical Considerations and Available Evidence
SSRIs are a commonly used medication. Although complications from them are not common because so many people take these medications, physicians will inevitably see problems such as dependence and withdrawal, hyponatremia, bleeding disorders, and even the uncommon but severe SSRI syndrome. To learn about these potential complications, we spoke with David Juurlink, MD, PhD, an internist and clinical pharmacologist at the University of Toronto.
Proton pump inhibitors are among the most commonly used medicines by patients. They’re generally safe, but they can cause acute kidney injury, and it’s important for clinicians to be aware of this potential complication. David Juurlink, MD, PhD, internist and clinical pharmacologist from the University of Toronto, discusses this important potential complication.
Related Article:
An Evidence-Based Approach to the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Although there are only about 4000 new cases of amyloidosis in the US per year, it can cause preserved ejection fraction heart failure, kidney and liver failure, and neuropathy. Amyloidosis is easily diagnosed and treatable, and it should be considered in the differential diagnosis for these diseases. Morie A. Gertz, MD, from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, talks with JAMA Clinical Reviews about amyloidosis.
Related:
Although frequently reported, penicillin allergy is actually uncommon. Penicillins are very effective against a wide variety of infections, and when they can't be used, problems arise. We discussed the problem of penicillin allergy with David Juurlink, MD, PhD, internist and clinical pharmacologist from the University of Toronto.
Related Article(s):
One of the most common causes for problems we see in manuscripts at JAMA is an inappropriately calculated study sample size. This seemingly mysterious process is explained by Lynne Stokes, PhD, professor of Statistical Science at Southern Methodist University in Dallas, Texas.
Generalizability of randomized trials is always limited because of the super-selectivity of the patients enrolled in these trials and the very controlled conditions in which clinical care is delivered. Pragmatic trials are performed in order to provide guidance for how to best deliver clinical care in situations that more closely resemble actual clinical scenarios. Hal Sox, MD, director of peer review for the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), explains how these trials work and what clinical questions they answer.
Related:
Pragmatic Trials: Practical Answers to “Real-world” Questions
Nearly 10% of all patients seen in primary care have depression. Although usually mild, when depression is severe the consequences can be serious. Tom Garrick, MD, professor of Psychiatry at the University of Southern California, discusses the diagnosis and treatment of depression.
Related:
Even limited hearing loss might be associated with cognitive decline. If true, early intervention with hearing aids might help people have better cognitive performance. Michael Johns III, MD, online editor for JAMA Otolaryngology, speaks with Justin Golub, MD, assistant professor of otolaryngology at Columbia University, whose research has shown that very mild hearing loss can be associated with cognitive disability.
When she was a teenager Melissa Red Hoffman's father was killed by terrorists. Dr Hoffman recalls her father's death and how that has influenced her career and how she can identify with patients and their families at the most difficult moments.
Read the story:
Management of COVID-19-related respiratory failure differs from what is necessary for ARDS. Rather than having alveolar edema, COVID-19 patients have pulmonary vascular dysregulation. Gas exchange is severely compromised with little reduction in lung compliance. Ventilatory support for COVID-19 patients requires higher than normal tidal volumes with minimal PEEP and allowance for higher than usual serum CO2 levels. How the unique pathophysiology of respiratory failure should be treated is discussed by John J. Marini, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota.
More than 6 million people worldwide have Parkinson disease. Even though it is classically associated with tremors, the disease has many manifestations and is very treatable for most patients. Michael S. Okun, MD, from the Department of Neurology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, discusses the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Parkinson disease.
Related:
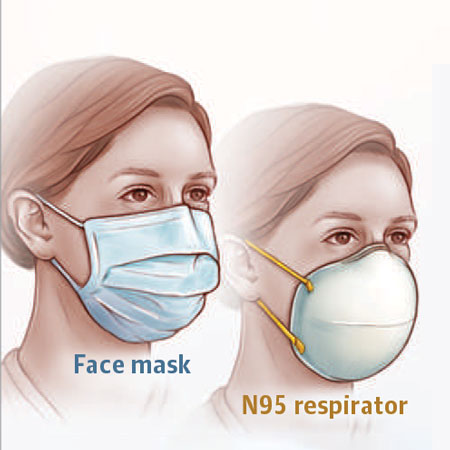
Shortages of face masks and N95 respirators have forced clinicians and hospitals to reuse these normally disposable items. Ron Shaffer, PhD, former CDC PPE Research Branch Chief, discusses effective sterilization techniques and how to test that the equipment stays protective after sterilization.
Eczema is extremely common in children. Most the time it is easily treated with topical steroids but on occasion it requires systemic therapies. JAMA Pediatrics Editor Dimitri Christakis, MD, MPH, and JAMA Network Open Editor Frederick Rivara, MD, MPH, discuss the results of a clinical trial of a new monoclonal antibody intended to improve eczema in children that was published in the January 2020 issue of JAMA Pediatrics.
Related:
Are Bacteria Transplants the Future of Eczema Therapy?
Persistence of Childhood Eczema Into Adulthood
Association Between Eczema and Stature in 9 US Population-Based Studies
Management of Atopic Dermatitis
Anti-IgE Medication Lessens Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis Severity
Food and medicine shopping is essential during the COVID-19 pandemic, but requires getting out and standing close to strangers at a time when social distancing and sheltering-in-place are recommended to slow spread of disease. David Aronoff, MD, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, explains how to minimize COVID-19 risk while shopping.
The lack of availability of COVID-19 testing has interfered with the ability to contain the spread of disease. Omai Garner, PhD, laboratory director for Clinical Microbiology in the UCLA health system, explains how PCR testing for COVID-19 works and why testing is in short supply.
In 2003, Toronto was the North American center for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). The disease spread through the city’s hospitals before anyone knew what was happening. Dr Allison McGeer was a clinician caring for SARS patients and ultimately was infected herself. She describes her experience as a patient and provider and reviews lessons learned that might help others manage their regional COVID-19 outbreaks.
Related:
Supporting the Health Care Workforce During the COVID-19 Global Epidemic
As COVID-19 spreads, clinicians and health systems are struggling to prepare for a surge of patients. Richard Stone, MD, the US Veterans Health Administration's Executive in Charge, spoke with JAMA about how the VA health system is preparing for this public health emergency.
Chloroquine was shown in 2004 to be active in vitro against SARS coronavirus but is of unproven efficacy and safety in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. The drug's potential benefits and risks for COVID-19 patients, without and with azithromycin, is discussed by Dr. David Juurlink, head of the Division of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is becoming more frequent as the population becomes more obese. This is not a benign problem, and NASH can ultimately lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. It is thought that NASH will ultimately become the most common cause for liver transplant. NASH is usually diagnosed as an incidental finding, but once found requires careful monitoring and patient counseling. Lisa N. Kransdorf, MD, MPH, from UCLA Health in California, discusses the diagnosis and management of NASH from a primary care clinician's perspective.
Hyperparathyroidism is a fairly common disease that causes elevated calcium levels and bone depletion, resulting in fractures and kidney problems. There are medications that can effectively manage hyperparathyroidism, and in some cases surgery is indicated. Michael Yeh, MD, professor and chief of endocrine surgery at UCLA, discusses the management of hyperparathyroidism.
Emerging information about how SARS-CoV-2 virus infects cells has led to speculation that NSAIDs and ACE inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may worsen clinical disease. Infectious disease physician Carlos del Rio, MD, of Emory University explains the concerns and their clinical implications.
Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress. After the war when food became more available CVD death rates went back up, resulting in Pritikin concluding that CVD was related to diet. Pritikin devised his own very low-fat diet that bears his name and the diet is still in use 65 years later.
Related:
This podcast explains the Pritikin diet to patients. Nathan Pritikin was a college dropout who became an entrepreneur. While doing research for the government during World War II, he observed that populations that had extremely limited food availability because of the war had substantially reduced mortality from cardiovascular disease—something unexpected at a time when cardiovascular disease was thought to be due to stress. After the war when food became more available CVD death rates went back up, resulting in Pritikin concluding that CVD was related to diet. Pritikin devised his own very low-fat diet that bears his name and the diet is still in use 65 years later.
Related:
Seattle was one of the first US cities to have a COVID-19 outbreak, with a cluster of nursing home-related deaths. However, many people who tested positive for the novel coronavirus never became ill, and in some the clinical illness was indistinguishable from influenza. John Lynch, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician and medical director for infection prevention and control at the Harborview Medical Center, summarizes his hospital’s experience managing the patients and outbreak.
Seattle has been a focal point for the US in the coronavirus pandemic. Doug Paauw, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, in Seattle, describes the UW primary care clinic experience as this pandemic evolved. Major lessons learned included accommodating for significant numbers of staff not available to work in the clinic because of school closures, change in workflow because of shortages of personal protective equipment, physicians having to accommodate very large numbers of patient queries via telephone, email, or electronic health record, and the importance of the rapid development of local ability to test for SARS-CoV-2 independent of public health agencies.
Coronovirus (the virus SARS-CoV-2) continues to spread throughout the world. In recent weeks, there has been an increasing number of cases and deaths in the US. As concern about the virus increases, there is an increasing need for accurate information about the disease and how much concern we should have. Anthony Fauci, MD, is the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and has been the main spokesperson for the US government about coronavirus. Dr Fauci spoke with JAMA Editor in Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, about where we are as of today with the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic.
Physicians who act out cause all sorts of problems. Fortunately, only a few clinicians have behavior problems and in the modern era, bad behaviors are not tolerated. Bad behaviors get reported these days and actions are taken against these sorts of clinicians. Clinicians who act out frequently say they are doing so to protect their patients. But are they? William Cooper, MD, MPH, and Gerald B. Hickson, MD, from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, discuss a study they published in relating bad behaviors to having more complications of surgical care.
Related article:
Although coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) dominates the news in early 2020, it affects few people in the US. In contrast, at the same time the US is experiencing a severe influenza epidemic, which has caused an estimated 250 000 hospitalizations and 14 000 deaths. Timothy Uyeki, MD, lead for the CDC’s 2019 novel coronavirus response team and Chief Medical Officer of CDC’s influenza division, discusses influenza in the US, how it compares to coronavirus, and what both patients and clinicians should know about this year’s flu season.
Great strides have been made in treating HIV, as Anthony Fauci, MD, discusses in this podcast episode. But even substantial viral suppression leaves some virus behind, causing chronic inflammation. Many chronic diseases, including atherosclerotic coronary vascular disease, are worsened by this chronic inflammatory state. Because HIV patients are now living very long lives, they are also developing chronic diseases at a more rapid rate than their non-HIV-infected peers because of this chronic inflammation.
More than 6 million people worldwide have Parkinson disease. Even though it is classically associated with tremors, the disease has many manifestations and is very treatable for most patients. Michael S. Okun, MD, from the Department of Neurology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, discusses the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Parkinson disease.
Related article:
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death in women. Some women have a cancer susceptibility gene known as BRCA, and women should be tested for BRCA under some circumstances. Carol Mangione, MD, division chief of General Internal Medicine and Health Services Research at UCLA, discusses when testing is appropriate, and Ranjit Manchanda, MD, PhD, from Barts Cancer Institute in London, UK, discusses the cost-effectiveness of BRCA screening for women who have had breast cancer.
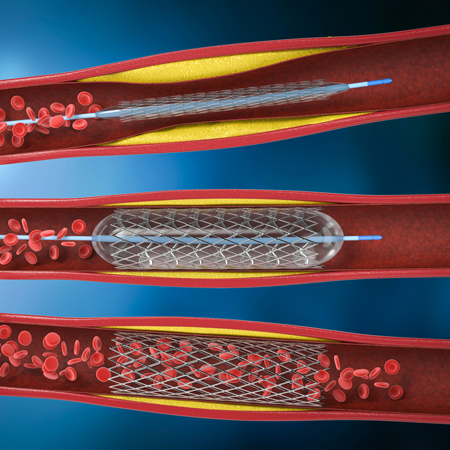
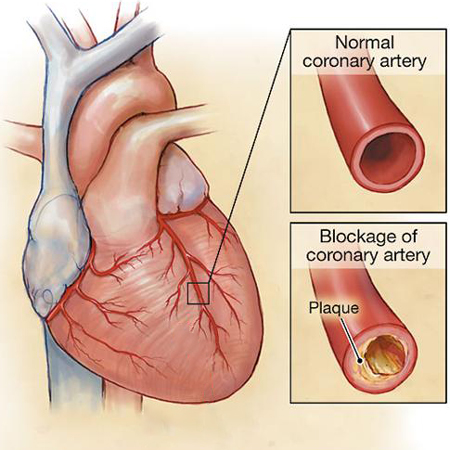
Controversy exists regarding how to best manage chronic stable angina. Intuitively, it seems that because it is usually caused by coronary artery lesions, addressing those lesions either via percutaneous coronary angiography or coronary artery bypass operations would be the best way to manage this problem. Several studies have suggested that this is not the case and that results of these interventions are no better than optimal medical management. Recently, a very large trial examining this clinical question has provided results suggesting that any approach works about the same. We interviewed Donald Lloyd-Jones, MD, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University, during the recent American Heart Association meeting about this issue.
Related articles:
Baseline Characteristics and Risk Profiles of Participants in the ISCHEMIA Randomized Clinical Trial
Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Causing Cardiac Ischemia in Women
Acupuncture as Adjunctive Therapy for Chronic Stable Angina: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Conjunctivitis and dry eye disease are some of the most common conditions patients present with. They are usually benign entities that respond well to conservative measures and usually don’t require medications. However, if medications are necessary, clinicians can find a comprehensive assessment of these drugs recently published in the December 2, 2019, issue of The Medical Letter. An excerpt from this article summarizing information about conjunctivitis and dry eye disease was published in the February 4, 2020 issue of JAMA. Kathryn Colby, MD, PhD, chair of the Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Science at the University of Chicago, explains in this podcast how to treat conjunctivitis and dry eye disease.